Revealing the development of local hollowings in rinnenkarren using field data (Totes Gebirge, Austria) and simulation of different numbers of channel junction
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3986/ac.v52i1.10832Keywords:
rinnenkarren, tributary channel, local hollowing, cross-section increase, CFD simulation, vorticityAbstract
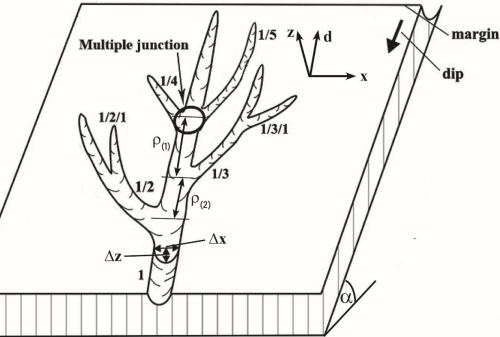
The development of emerging hollowing parts of the main channels of rinnenkarren systems at tributary channel junctions is interpreted in this study using Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulation. In the field, data from cross-sections of 505 local hollowings with one or more tributary channel junctions were investigated. The shift in the width–depth ratio of the local hollowings was studied as the number of junctions and the size of the hollowing changed. Flow was simulated through CFD in digital model channels, and the nature of the resulting vorticity was interpreted. Field data show that local hollowings emerging in the main channels of the channel systems at the junctions. In the main channels, when only a few tributary channels join in the vicinity of each other, local hollowings deepen during their growth and, most often, gradually become pits (depth is larger than width), as the morphometric analysis suggests. As the number of tributary channels increases, the local hollowing may develop into a kamenitza (width is larger than depth). The model experiment suggests the explanation that more tributary channel junctions result in more extensive vorticity, which contributes to the lateral extension (widening) of this channel section. The distance of the tributary junctions from each other also influences the downstream dimension of the local hollowing. In the field, the larger this distance, the more separated the local hollowings induced by individual tributaries. The model experiment suggests that this may occur because the intense vorticity generated by individual junctions becomes increasingly sectionalized as the tributary channel density decreases.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors guarantee that the work is their own original creation and does not infringe any statutory or common-law copyright or any proprietary right of any third party. In case of claims by third parties, authors commit their self to defend the interests of the publisher, and shall cover any potential costs.
More in: Submission chapter




