Influence of Geological Structure on Micro-location of Submarine Karstic Sulphur Springs near Izola (SW Slovenia)
Vpliv geološke strukture na mikrolokacijo podmorskih kraških žveplenih izvirov pri Izoli (JZ Slovenija)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3986/ac.v52i1.11091Keywords:
sulphur, karst springs, Adria foreland, Izola anticline, geological mappingAbstract
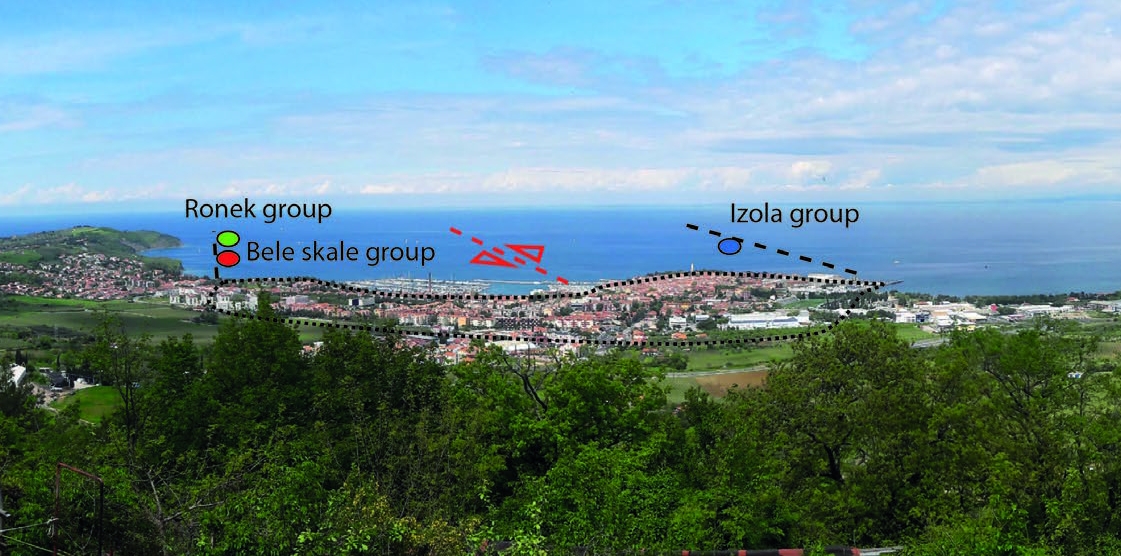
In the Slovenian part of the Gulf of Trieste/Trst, submarine springs occur as funnel-shaped depressions in the Holocene sandy-silt marine sediment that forms the seafloor. These springs exhibit both elevated temperatures (up to 29.6 °C) and sulphur content. Based on their location, they are divided into three groups: the Izola group (three springs), the Bele skale group (two springs), and the Ronek group (seven springs). Previous investigations linked these springs to the Izola anticline, characterized by its limestone core and flysch limbs, but no detailed explanation was provided. We propose that: A) sulphur groundwater springs from the limestone (karstic aquifer) at the stratigraphic boundary with the flysch and B) springs occur in the nearshore area, where the sedimentary cover of Quaternary deposits is thin enough to be penetrated by spring waters and washed out. According to existing data, the anticline axis is NW-SE directed, and the Izola group lies approximately on the seaward extension of the axis. Therefore, this interpretation fits perfectly for the Izola group, while the Ronek and Bele skale groups are off-axis extensions and require reinterpretation. In order to resolve the micro-locations of the Ronek and Bele skale groups, we conducted a sedimentological logging of the flysch deposits and detailed geological mapping. The investigations revealed that: A) limestone outcrops occur only in the town of Izola, B) two prominent calciturbidite megabeds that occur in the flysch enable very detailed geological mapping, and C) the axis of the Izola anticline is oriented in the WNW-ESE direction, and this moderate anti-clockwise rotation of the anticline axis explains the micro locations of all springs. The Ronek and Bele skale groups are located on the southern side, and the Izola group is on the northern side of the limestone core of the Izola anticline.
Downloads
References
Allmendinger, R. W., Cardozo, N., Fisher, D., 2011, Structural geology algorithms: Vectors and tensors. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 302pp.
Benedik, A., Rožič, B., 2002. Hidrogeološko poročilo o rezultatih raziskav za zajem termalne vode v globokem vodonosniku na območju Izole z vrtino LIV-1. Poročilo geo-hidro d.o.o., Drenov grič, 16 pp. (in Slovenian)
Busetti, M., Volpi, V., Barison, E., Giustiniani, M., Marchi, M., Ramella, R., Wardell, N., Zanolla, C., 2010a. Meso-Cenozoic seismic stratigraphy and the tectonic setting of the Gulf of Trieste (northern Adriatic). GeoActa, SP 3: 1–14.
Busetti, M., Volpi, V., Nicolich, R., Barison, E., Romeo, R., Baradello, L., Brancatelli, G., Giustiniani, M., Marchi, M., Zanolla, C., Wardell, N., Nieto, D., Ramella, R., 2010b. Dinaric tectonic features in the Gulf of Trieste (Northern Adriatic Sea). Boll. di Geofis. Teor. ed Appl., 51: 117–128.
Cardozo, N., Allmendinger, R.W., 2013. Spherical projections with OSXStereonet. Computers & Geosciences, 51: 193 – 205. doi:10.1016/ j.cageo.2012.07.021.
Covelli, S., Fontolan, G., Faganeli, J., Ogrinc, N., 2006. Anthropogenic markers in the Holocene stratigraphic sequence of the Gulf of Trieste (northern Adriatic Sea). Mar. Geol. 230: 29–51. doi:10.1016/j.margeo.2006.03.013
Čar, J., 2018. Geostructural mapping of karstified li¬mestones. Geologija, 61/2: 133–162. DOI: 10.5474/ geologija.2018.010
Drobne, K., Ogorelec, B., Pavšič, J., Pavlovec, R., 2009. Paleocene and Eocene in south-western Slovenia. In: Pleničar, M., Ogorelec, B., Novak., M. (Eds.), The geology of Slovenia. Geological Survey of Slovenia, Ljubljana, pp. 311-372.
Faganeli, J., Ogrinc, N., Walter, L. N., & Žumer, J., 2005. Geochemical characterization of the submarine spring of Izola (Gulf of Trieste, N Adriatic Sea). RMZ - Materials and Geoenvironment, 52: 35–39.
Falace, A., Kaleb, S., Orlando-Bonaca, M., Mavrič, B., Lipej, L., 2011. First contribution to the knowledge of coralline algae distribution in the Slovenian circalittoralzone (Northern Adriatic). Annales Series Historia Naturalis, 21(1): 27-40.
Jurkovšek, B., Cvetko Tešović, B., Kolar-Jurkovšek, T., 2013. Geology of Kras. Geološki zavod Slovenije, Ljubljana, 205pp.
Jurkovšek, B., Biolchi, S., Furlani, S., Kolar-Jurkovšek, T., Zini, L., Jež, J., Tunis, G., Bavec, M., Cucchi, F., 2016. Geology of the Classical Karst Region (SW Slovenia–NE Italy). J. Maps, 1–12. doi:10.1080/17445647.2016.1215941
Kovač, N., Glavaš, N., Ramšak, T., Dolenec, M., Rogan Šmuc, N., 2018. Metal(oid) mobility in a hypersaline salt marsh sediment (Sečovlje Salina, northern Adriatic, Slovenia). Science of the total environment 644: 350–359.
Kramar, J., 2003. Izola: Mesto ribičev in delavcev. Zgodovinsko društvo za južno Primorsko, Koper, 629 pp. (in Slovenian)
Novak, A., Šmuc, A., Poglajen, S., Vrabec, M., 2020. Linking the high-resolution acoustic and sedimentary facies of a transgressed Late Quaternary alluvial plain (Gulf of Trieste, northern Adriatic). Mar. Geol. 419: 106061. doi:10.1016/j.margeo.2019.106061
Lapanje, A., 2006. Origin and chemical composition of thermal and thermomineral waters in Slovenia. Geologija 49(2): 347–370.
Lipej, L., Orlando-Bonaca M., Mavrič, B., 2016. Biogenic formations in the Slovenian sea. National Institute of Biology, Marine Biology Station, Piran, 206 pp.
Ogorelec, B., Mišič, M., Faganeli, J., Stegnar, P., Vrišer, B., Vukovič, A., 1987. Recentni sediment Koprskega zaliva. Geologija, 30: 87–121.
Ogorelec, B., Mišič, M., Šercelj, A., Cimerman, F., Faganeli, J., Stegnar, P., 1981. Sediment sečoveljske soline. Geologija 24: 180–216.
Ogorelec, B., Faganeli, J., Mišič, M., Čermelj, B., 1997. Reconstruction of paleoenvironment in the Bay of Koper (Gulf of Trieste, Northern Adriatic). Annales 11: 187–200.
Ogorelec, B., Mišič, M., Faganeli, J., 1991. Marine geology of the Gulf of Trieste (northern Adriatic): Sedimentological aspects. Mar. Geol., 99: 79–92. doi:10.1016/0025-3227(91)90084-H
Orlando-Bonaca, M., Mavrič, B., Lipej, L., Kaleb, S., Falace, A., 2017. Coralline algae on biogenic formations in marine waters off Slovenia (northern Adriatic Sea). Ann. Ser. Hist. Nat., 27: 89–96.
Pavlovec, R., 1985. Numulitine iz apnencev pri Izoli (SW Slovenija). (Nummulitines from limestones at Izola, Istria, W Yugoslavia). Razprave 4. razr. SAZU 26: 219–230.
Pavlovec, R., Pavšič, J., 1987. Biostratigrafija plasti z rakovicami v Istri. Geologija, 28/29: 55-68. (with English Summary)
Pavšič, J., Peckmann, J., 1996. Stratigraphy and Sedimentology of the Piran Flysch Area (Slovenia). Annales 9: 123–138.
Placer, L., 2005. Structural curiosity of the northern Istria, Geologija, 48/2: 245–251.
Placer, L., 2007. Kraški rob (landscape term): geologic section along the motorway Kozina - Koper (Capodistria). Geologija, 50/1: 29–44.
Placer, L., Košir, A., Popit, T., Šmuc, A., Juvan, G., 2004. The buzet thrust fault in istria and overturned carbonate megabeds in the Eocene flysch in the Dragonja Valley (Slovenia). Geologija, 47: 193–198. doi: 10.5474/geologija.2004.015
Placer, L., Vrabec, M., Celarc, B., 2010. The bases for understanding of the NW Dinarides and Istria Peninsula tectonics. Geologija, 53(1): 55–86.
Pleničar, M., Polšak, A., Šikić, D., 1973. Osnovna geološka karta SFRJ. 1:100.000. Tolmač za list Trst : L 33-88. (Explanatory book to the Basic Geological Map of SFRJ), Zvezni geološki zavod, Beograd.
Pleničar, M., Polšak, A., Šikić, D., 1969. Osnovna geološka karta SFRJ. L 33-88, Trst. (Basic Geological Map of SFRJ), Zvezni geološki zavod, Beograd.
Romeo, R., 2009. Studio geofisico integrato ad alta risoluzione dei depositi marini e della struttura del substrato della Riviera di Miramare (Golfo di Trieste). University of Trieste.
Šušmelj, K., Žvab Rožič, P., Vreča, P., Kanduč, T., Verbovšek, T., Nagode, K., Zuliani, T., Čenčur Curk, B., Rožič, B., Čermelj, B., 2022. Hidrogeokemične in izotopske raziskave podmorskih in kopenskih izvirov pri Izoli. In: Kuhar, M. (Ed.), Raziskave s področja geodezije in geofizike 2021. University of Ljubljana, Faculty of Civil and Geodetic Engineering, Ljubljana, pp. 55-64.
Šušteršič, F., 2006. Relationships between deflector faults, collapse dolines and collector channel formation: some examples from Slovenia. International Jour¬nal of Speleology, 35: 1–12. doi: 10.5038/1827- 806X.35.1.1
Šušteršič, F., Čar, J., Šebela, S., 2001. Zbirni kanali in zaporni prelomi − Collector channels and deflector faults. Naše jame, 43: 8–22. (In Slovene, English Summary)
Trincardi, F., Argnani, A., Correggiari, A., Foglini, F., Rovere, M., Angeletti, L., Asioli, A., Campiani, E., Cattaneo, A., Gallerani, A., Piva, A., Remia, A., Ridente, D., Taviani, M., 2011a. Note illustrative della Carta Geologica dei mari italiani alla scala 1:250.000 foglio NL 33-7 Venezia.
Trincardi, F., Correggiari, A., Cattaneo, A., Remia, A., Taviani, M., Angeletti, L., Foglini, F., Campiani, E., 2011b. Carta Geologica dei mari italiani alla scala 1:250.000 foglio NL 33-7 Venezia.
Trobec, A., Busetti, M., Zgur, F., Baradello, L., Babich, A., Cova, A., Gordini, E., Romeo, R., Tomini, I., Poglajen, S., Diviacco, P., Vrabec, M., 2018. Thickness of marine Holocene sediment in the Gulf of Trieste (northern Adriatic Sea). Earth Syst. Sci. Data, 10: 1077–1092. doi:10.5194/essd-10-1077-2018
Trobec, A., Šmuc, A., Poglajen, S., Vrabec, M., 2017. Submerged and buried Pleistocene river channels in the Gulf of Trieste (Northern Adriatic Sea): Geomorphic, stratigraphic and tectonic inferences. Geomorphology, 286: 110–120. doi:10.1016/j.geomorph.2017.03.012
Vrabec, M., Busetti, M., Zgur, F., Facchin, L., Pelos, C., Romeo, R., Sormani, L., Slavec, P., Tomini, I., Visnovic, G., Žerjal, A., 2014. Refleksijske seizmične raziskave v slovenskem morju SLOMARTEC 2013. In: Kuhar, M., Čop, R., Gosar, A., Kobold, M., Kralj, P., Malačič, V., Rakovec, J., Skok, G., Stopar, B., Vreča, P. (Eds.). Raziskave s Področja Geodezije in Geofizike 2013. University of Ljubljana, Faculty of Civil and Geodetic Engineering, Ljubljana, pp. 97–101.
Vrabec, M., Rožič, B., 2014. Strukturne in sedimentološke posebnosti obalnih klifov. In: Rožič, B., Verbovšek, T., Vrabec M. (Eds.), 4. Slovenian Geological Congress, Abstracts and Field Trips, Faculty of Natural Sciences and Engineering, Ljubljana, pp. 84–91.
Žumer, J., 2004. Odkritje podmorskih termalnih izvirov pred Izolo. Geografski obzornik: časopis za geografsko vzgojo in izobraževanje, 51/2: 11–17.
Žumer, J., 2008. Podmorski kraški izviri pred Izolo. Naše jame, 47: 39-44.
Žvab Rožič, P., Verbovšek, T., Kanduč, T., Zuliani, T., Čenčur Curk, B., Šušmelj, K., Vreča, P., 2021. Hydrogeochemical and isotopic characteristics of thermal sulphur springs along the Slovenian coast. In: Inspiring groundwater : 48th IAH congress, Brussels, Belgium, 2021 : IAH2021, book of abstracts. Brussels: IAH, pp. 170-171.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors guarantee that the work is their own original creation and does not infringe any statutory or common-law copyright or any proprietary right of any third party. In case of claims by third parties, authors commit their self to defend the interests of the publisher, and shall cover any potential costs.
More in: Submission chapter




