Staging in the hypergene transformation of sulphate and carbonate rocks (based on slide-rocks under organ tubes in Kungur Ice Cave)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3986/ac.v44i2.610Abstract
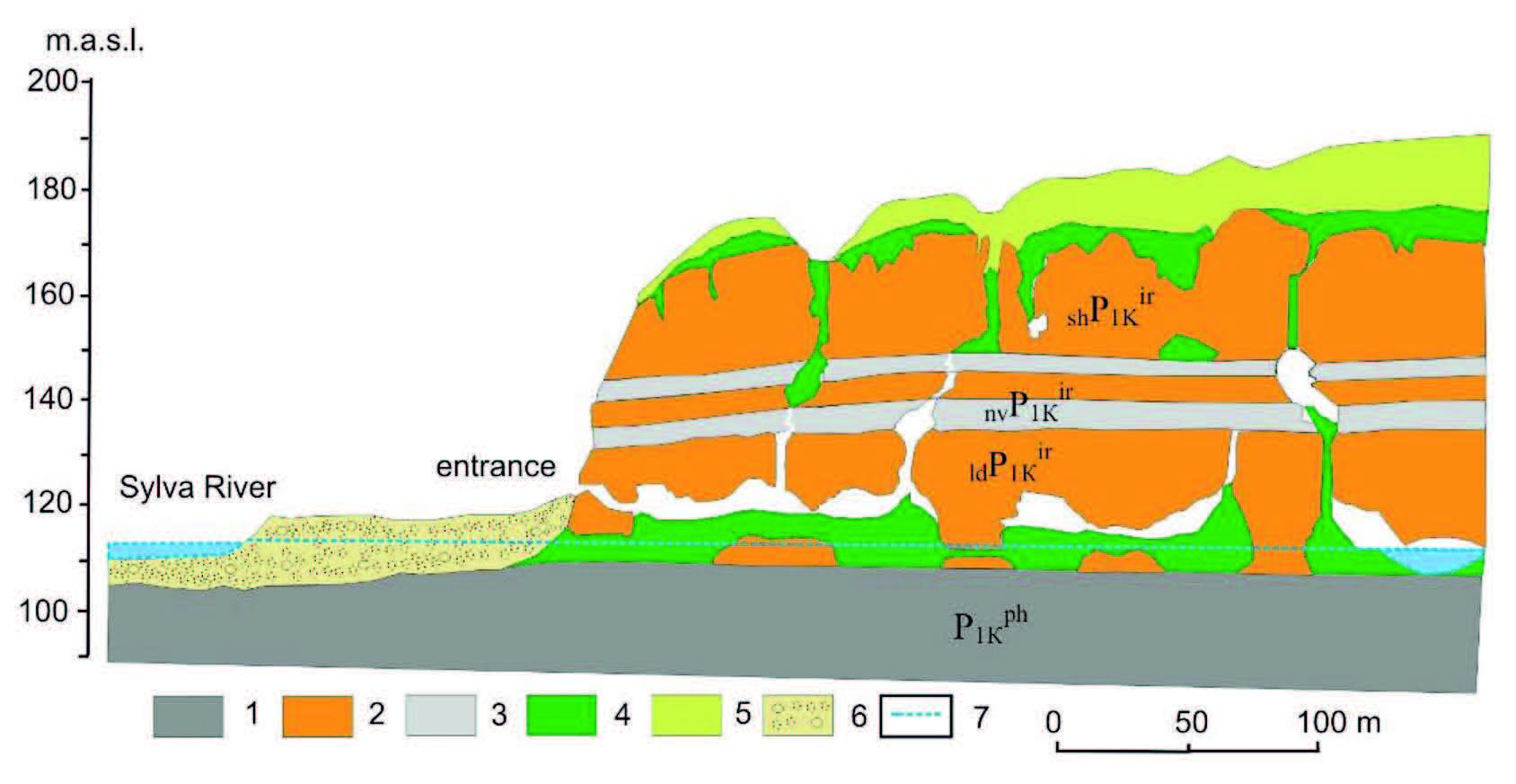
The article describes the influence of microclimate on the constitution of talus cone deposits in the grottoes of Kungur Ice Cave. Deposits of slide-rocks collapsed from «organ tubes» in different climatic zones of the cave were investigated. It was established that slide-rock material has identical initial composition, but is transformed in different ways depending on the microclimate in which it is deposited. In the cold zone of the cave, with temperatures below 0 °C control («freeze») the transformation of carbonate and sulphate materials. The main processes of mineral formation in cold zone are connected with cryogenic mineralization from sulphate and carbonate waters. Slide-rocks in the transition zone of the cave, where temperatures range from 0 °C to 3 °C, are distinguished by the presence of authigenic carbonate breccias and a variety of gypsum forms. In the warm zone of the cave, slide-rock undergoes complete dissolution of gypsum and partial dissolution of carbonate debris. In the future changes of paleoclimatic conditions in the karst cavity can be identified by investigation of deposits that are climatic markers.
Vpogled v hipergeno preobrazbo sulfatnih in karbonatnih kamnin (temelječ na polzečih odlomkih kamnine pod »orgelskimi cevmi« v Kungurski ledeni jami)
Članek opisuje vpliv mikroklime na oblikovanje talusnega stožca v rovih Kongurske ledene jame. Preiskovani so bili polzeči nakopičeni odlomki kamnine, ki so odpadli iz sten tako imenovanih »orgelskih cevi« v različnih klimatskih območjih jame. Ugotovljeno je bilo, da ima polzeči material enako začetno sestavo, vendar se preoblikuje na različne načine, odvisno od mikroklime v kateri se nalaga. V hladnih delih jame, temperature pod 0 °C kontrolirajo (zmrzovanje) preoblikovanje karbonatnih in sulfatnih materialov. Glavni procesi nastajanja mineralov v mrzlih območjih so povezani s kriogeno mineralizacijo iz sulfatnih in karbonatih vod. Polzeče odlomke kamnine v prehodnih delih jame, kjer temperature nihajo med 0 °C do 3 °C, zaznamujejo prisotnost avtigenih karbonatnih breč in raznolike oblike sadre. V toplih delih jame, so polzeči odlomki kamnine podvrženi popolni raztopitvi sadrinih in delni raztopitvi karbonatnih klastov. V prihodnosti se bo lahko zaznavalo spremembe mikroklime v kraških jamah z raziskavami talusnih sedimentov, ki so odlični klimatski markerji.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Authors guarantee that the work is their own original creation and does not infringe any statutory or common-law copyright or any proprietary right of any third party. In case of claims by third parties, authors commit their self to defend the interests of the publisher, and shall cover any potential costs.
More in: Submission chapter




