Hydrochemical variations of the springs on Jinfo Mountain, Chongqing, China
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3986/ac.v44i1.798Povzetek
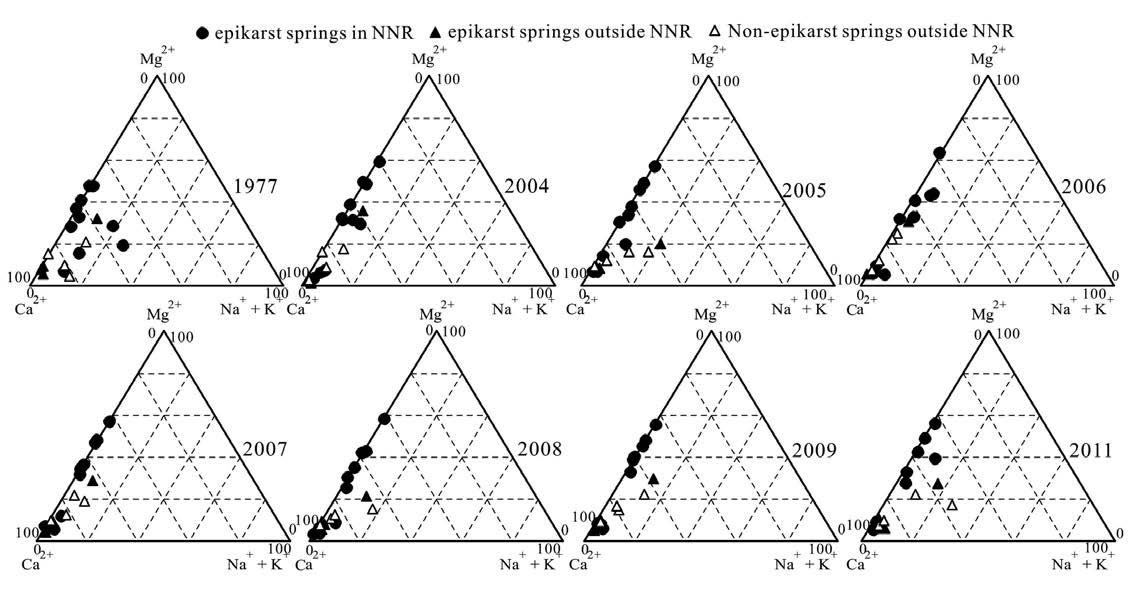
There are 18 springs within the Jinfo Mountain area of Chongqing, SW China (of which 10 epikarst springs are within the National Nature Reserve, and 4 epikarst springs and 4 non-epikarst springs are outside the National Nature Reserve). The hydrochemical characteristics of these springs were measured in 1977, 2004-2009, and 2011. The data show that the hydrochemistry type of springs in different areas, and for different years, is Ca-HCO3 and Ca-HCO3-SO4, whereas the concentrations of SO4 and NO3 are very sensitive to changes in human activities. All the springs with the highest SO4 and NO3 concentrations in the study area showed minimum concentrations in 1977 and an upward trend in concentrations from 2004 to 2008, followed by a period of lower concentrations. Springs with low SO4 and NO3 concentrations were distributed solely at the top of Jinfo Mountain in the National Nature Reserve. The hydrochemical variations observed in springs on Jinfo Mountain demonstrate that the implementation of environmental policy measures and industrial restructuring have successfully contributed to environmental protection of the springs.Prenosi
Podatki o prenosih še niso na voljo.
Prenosi
Objavljeno
2015-07-09
Kako citirati
Qiong, X., Licheng, S., & Kunyu, W. (2015). Hydrochemical variations of the springs on Jinfo Mountain, Chongqing, China. Acta Carsologica, 44(1). https://doi.org/10.3986/ac.v44i1.798
Številka
Rubrike
Original papers
Licenca
Avtorji jamčijo, da je delo njihova avtorska stvaritev, da v njem niso kršene avtorske pravice tretjih oseb ali kake druge pravice. V primeru zahtevkov tretjih oseb se avtorji zavezujejo, da bodo varovali interese založnika ter da bodo povrnili morebitno škodo.
Podrobneje v rubriki: Prispevki




