Hydrologic Connections and Dynamics of Water Movement in the Classical Karst (Kras) Aquifer: Evidence from Frequement Chemical and Stable Isotope Samoling
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3986/ac.v37i1.163Povzetek
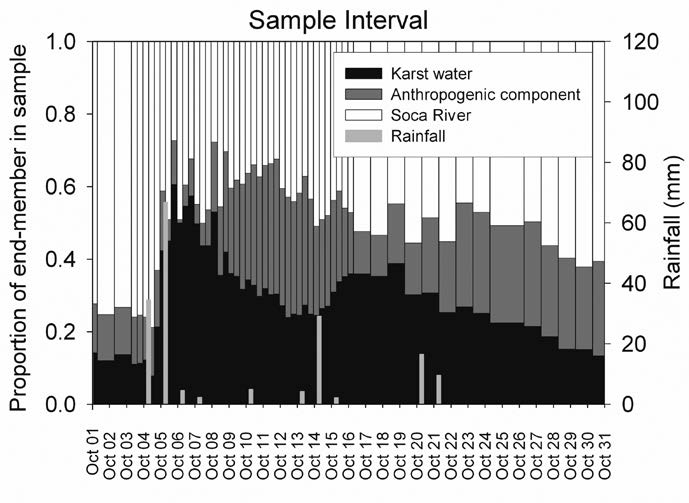
A review of past researchon the hydrogeology of the Classical Karst (Kras) region and new information obtained from a two-year study using environmental tracers are presented in this paper. The main problems addressed are 1) the sources of water to the Kras aquifer resurgence zone—including the famous Timavo springs—under changing flow regimes; 2) a quantification of the storage volumes of the karst massif corresponding to flow regimes defined by hydrographrecessions of the Timavo springs; and 3) changing dynamics between deep phreatic conduit flow and shallow phreatic and epiphreatic storage within the aquifer resurgence zone as determined throughchanges in chemical and isotopic composition at springs and wells. Particular focus was placed on addressing the long-standing question of the influence of the Soča River on the ground waters of the aquifer resurgence zone. The results indicate that the alluvial aquifer supplied by the sinking of the Soča River on the northwestern edge of the massif contributes approximately 75% of the mean annual outflow to the smaller springs of the aquifer resurgence zone, and as muchas 53% to the mean annual outflow of the Timavo springs. As a whole, the Soča River is estimated to contribute 56% of the average outflow of the Kras aquifer resurgence. The proportions of Soča River water increase under drier conditions, and decrease under wetter conditions. Time series analysis of oxygen stable isotope records indicate that the transit time of Soča River water to the Timavo springs, Sardos spring, and well B-4 is on the order of 1-2 months, depending on hydrological conditions. The total baseflow storage of the Timavo springs is estimated to be 518 million m3, and represents 88.5% of the storage capacity estimated for all flow regimes of the springs. The ratio of baseflow storage volume to the average annual volume discharged at the Timavo springs is 0.54. The Reka River sinking in Slovenia supplies substantial allogenic recharge to the aquifer; however, its influence on the northwest resurgence zone is limited to the Timavo springs, and is only a significant component of the spring discharge under flood conditions for relatively brief periods (several days to weeks). Sustainability of the trans-boundary aquifer of the Kras will benefit from maintaining highwater quality in the Soča River, as well as focused water tracing experiments within the epiphreatic zone of the aquifer to better delineate the recharge zone and to identify sources of potential contamination to the Brestovica water supply well.Prenosi
Podatki o prenosih še niso na voljo.
Prenosi
Objavljeno
2008-06-01
Kako citirati
Doctor, D. H. (2008). Hydrologic Connections and Dynamics of Water Movement in the Classical Karst (Kras) Aquifer: Evidence from Frequement Chemical and Stable Isotope Samoling. Acta Carsologica, 37(1). https://doi.org/10.3986/ac.v37i1.163
Številka
Rubrike
Original papers
Licenca
Avtorji jamčijo, da je delo njihova avtorska stvaritev, da v njem niso kršene avtorske pravice tretjih oseb ali kake druge pravice. V primeru zahtevkov tretjih oseb se avtorji zavezujejo, da bodo varovali interese založnika ter da bodo povrnili morebitno škodo.
Podrobneje v rubriki: Prispevki




