Carbon dioxide in the soils and adjacent caves of the Moravian Karst
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3986/ac.v39i3.76Abstract
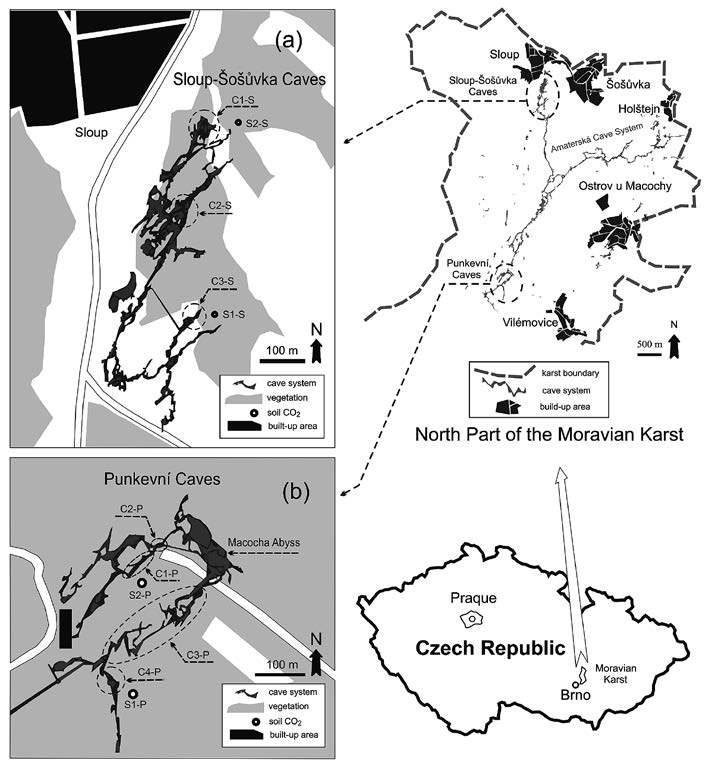
Variations of soil/cave CO2 concentrations and further variables suchas temperature, humidity, and cave visitor attendance were studied in two sites of the Moravian Karst (CzechRepublic). All the variables showed the same seasonality; they were strongly correlated witheachother. The dependence of soil CO2 levels on soil air temperature and absolute humidity was confirmed. Individual effects could not be distinguished because of multicollinearity. The effect of vegetation on soil CO2 production was not recognized. Cave attendance was identified as the most significant predictor of cave CO2 levels. Other variables, soil CO2 and temperature gradients, were less significant. A spurious relationship was alternatively considered, in whichexternal temperature was the universal predictor of cave CO2 levels.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Authors guarantee that the work is their own original creation and does not infringe any statutory or common-law copyright or any proprietary right of any third party. In case of claims by third parties, authors commit their self to defend the interests of the publisher, and shall cover any potential costs.
More in: Submission chapter




