Morphological features and formation conditions of The Almopia Speleopark caves (Loutra Almopias, N. Greece)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3986/ac.v50i1.7592Keywords:
Phreatic calcite, thermal water, hypogene speleogenesis, hydrothermal cave, Loutra Almopias Cave, GreeceAbstract
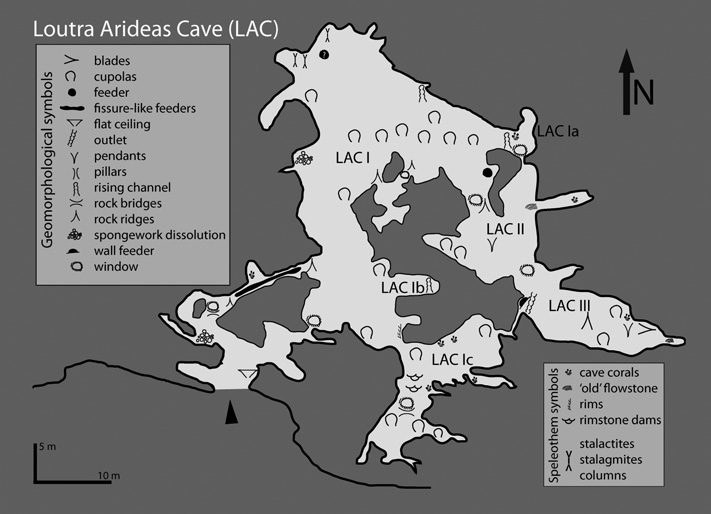
The Almopia Speleopark caves are located at the Almopia basin in northern Greece, at the foothill of Voras Mountain, and are formed in the Maestrichtian limestones of the Pelagonian zone. They are studied on the basis of their meso- and micro-scale morphology as well as their horizontal pattern, in order to investigate the character of the forming aquifer. Emphasis is given on the morphological description of the Loutra Almopias Cave. Cave morphology is dominated by the presence of cupolas, rock bridges, ridges and “windows”, abrupt terminations of fracture guided passages, pendants, rising channels, pseudonotches, false-floors and spongework. Speleogens indicate a speleogenesis due to slowly natural convecting hot water bodies. Phreatic calcite from the Varathron Cave is analyzed on the basis of the fluid inclusions in order to investigate the physicochemical conditions of the convecting water bodies. This has shown that the calcite was formed at temperatures ranging between 120 and 189 ºC, with a peak around 150 ºC. The fluids were dominated by NaCl of very low salinities (0.2-1.0 wt% NaCl equiv.), showing probably the incorporation of meteoric waters.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors guarantee that the work is their own original creation and does not infringe any statutory or common-law copyright or any proprietary right of any third party. In case of claims by third parties, authors commit their self to defend the interests of the publisher, and shall cover any potential costs.
More in: Submission chapter




