Hydraulic Properties of Carbonate Rocks from Slovakian Borehole Database
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3986/ac.v39i2.94Abstract
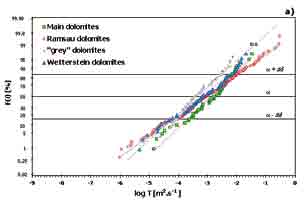
Using archival hard copy records on 22,922 wells and hydrogeological boreholes, maintained since 1950's on the territory of Slovak Republic, a spatial database was developed. If possible, each borehole was linked to a certain aquifer or aquifer lithological type, according to its screened interval. Wells with ambiguous position of open casing were excluded from further processing to obtain distinct relation of pumping rate to lithology. Using stored records of hydraulic tests, eachpumping rate was processed to obtain uniformly calculated “standard” specific capacity. These values were subsequently used to re-interpret hydraulic parameters. Based on standardized specific capacity data, estimates of transmissivity (T; in m2∙s-1) and hydraulic conductivity (K; in m∙s-1) for eachwell were calculated and linked to corresponding aquifer type. From these, hydraulic properties of limestones (238 boreholes), dolomites (463 boreholes) and granitoid rocks (96 boreholes) are compared. As anticipated, geometrical mean of transmissivity was low for granitoids (6.51∙10-5 m2∙s-1) and in one order of magnitude higher for limestones (6.16∙10-4 m2∙s-1), due to its enhancement by karstification. The highest observed value of mean transmissivity, two times higher than that found for limestones, was obtained for dolomitic aquifers (1.04∙10-3 m2∙s-1). Dolomitic aquifers also show the highest median values of hydraulic conductivity (3.21∙10-5 m∙s-1), in one order of magnitude higher than granitoids (2.10∙10-6 m∙s-1) and three times higher than limestones (9.45∙10-6 m∙s-1). In comparison with limestones, dolomites seem to be slightly more homogeneous in aquifer properties; also several lithological types there show similarities in both T and K. Some limestone lithofacies (Steinalm and Raming), seem to have lower transmissivity and hydraulic conductivity comparing to other limestones types (Dachstein, Gutenstein, Wetterstein). The data on hydraulic properties of all these hard rocks show lognormal statistical distribution and high heterogeneity.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Authors guarantee that the work is their own original creation and does not infringe any statutory or common-law copyright or any proprietary right of any third party. In case of claims by third parties, authors commit their self to defend the interests of the publisher, and shall cover any potential costs.
More in: Submission chapter




