Rayleigh wave and well head response to calculate porosity in the Edwards aquifer of south-central Texas, USA
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3986/ac.v49i2-3.8849Keywords:
Rayleigh wave, Poisson’s ratio, displacements,, well head, Gassmann equationAbstract
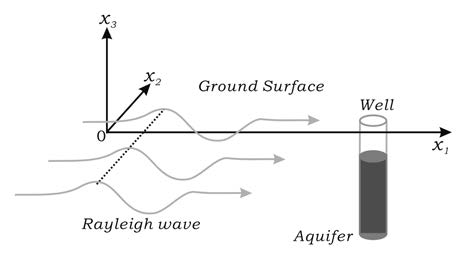
We use the magnitude and centroid period of Rayleigh wave along with the amplitude of fluctuations of water level in a well to calculate effective porosity of a karst aquifer at the site scale. The radial and vertical displacements of Rayleigh wave are first related to the confining pressure of rock, which is then related to fluid pressure via the Gassmann equation. Three seismograms recorded at station 633A of the USARRAY and the induced responses of Well J-17 in the Edwards Aquifer (Texas) allow the calculation of an effective porosity between 17.0 and 24.4 percent, the average of which is close to the total porosity of core samples determined by geophysical well logs. This paper provides an innovative method to measure effective porosity in aquifers. Because of the long wavelengths of Rayleigh wave, the interdisciplinary approach is advantageous in that the resulting effective porosity is at the site scale which includes large conduits or voids.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors guarantee that the work is their own original creation and does not infringe any statutory or common-law copyright or any proprietary right of any third party. In case of claims by third parties, authors commit their self to defend the interests of the publisher, and shall cover any potential costs.
More in: Submission chapter




