Determining the directions and characteristics of underground water flow in karst for the purpose of traffic routes construction: the case of the new Divača-Koper railway line (SW Slovenia)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3986/ac.v49i1.8582Keywords:
karst water, railway route, phreatic zone, tracer test, active cave streams, Classical KarstAbstract
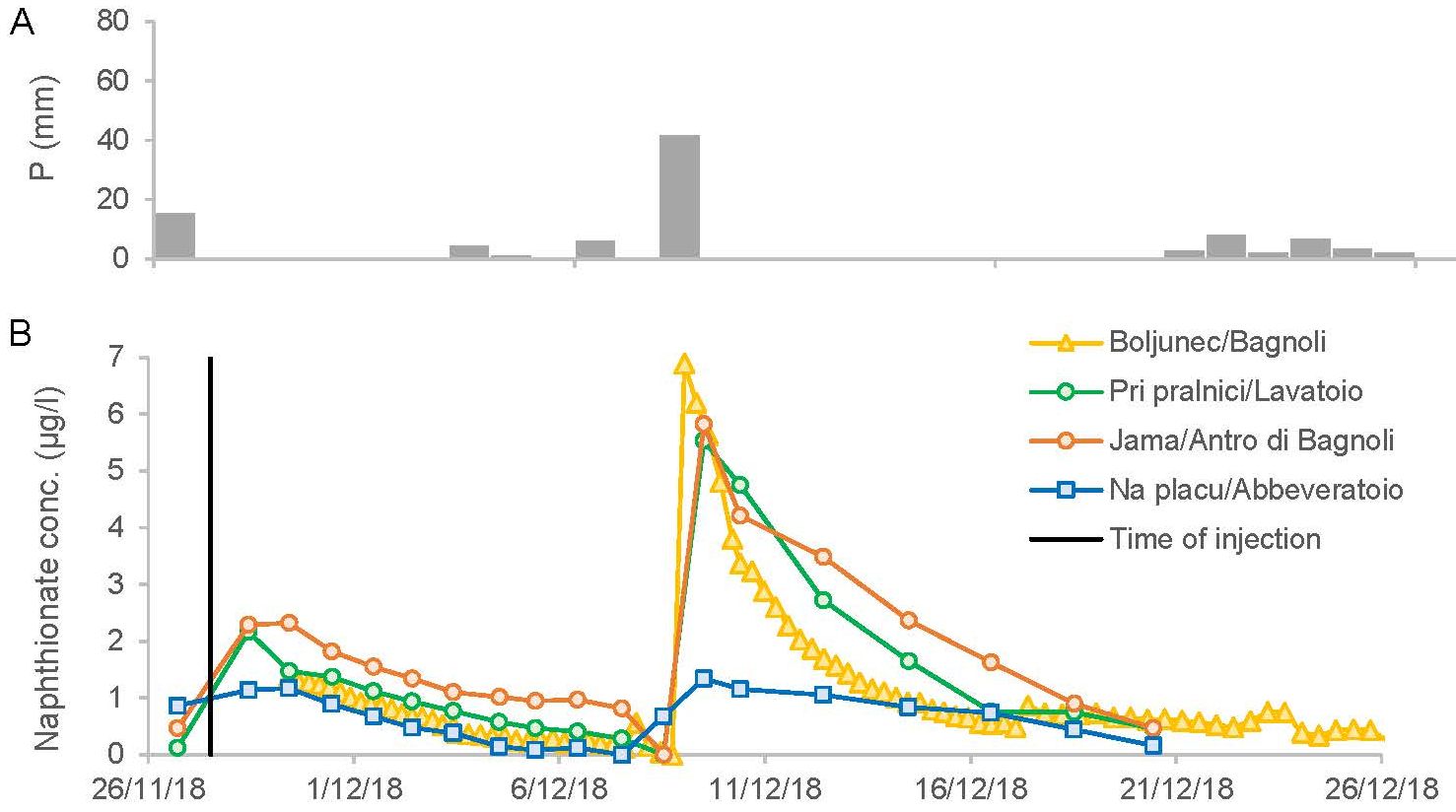
The new railway line between Divača and Koper/Capodistria in south-western Slovenia is being built, a part of which crosses the southern outskirts of the Classical Karst plateaux. It will run through two tunnels, the northern tunnel T1 (6.7 km long) and the southern T2 (6 km long), which partially cross karst aquifer system. A multi-tracer test with injections of fluorescent dyes uranine and naphthionate, bypassing the karst vadose zone, was carried out to define the directions and dynamics of the underground water flow. The main goals were better understanding of the complex hydrogeological conditions in the area and assessment of possible environmental impacts on the nearby water sources. With tracing of uranine injected into a nearby cave stream, the direction of flow from the northern T1 tunnel mainly towards the Reka-Timavo aquifer system and further towards the Timava/Timavo springs was proved. The peak velocities, as determined from the peaks of the tracer breakthrough curves, range from 29 m/h to 36 m/h. Through the wider and well-connected conduits of the Reka-Timavo system, the peak velocities can reach up to 88 m/h. The recovery of uranine in an intermediate cave, i.e., Jama 1 v Kanjaducah, amounted to approximately 74 %. The northern section of the southern T2 tunnel is a part of a wider bifurcation zone between the Osapska Reka and the Boljunec/Bagnoli springs, where peak flow velocities between 10 and 13 m/h have been determined by tracing of naphthionate injected into a borehole located in the line of the planned tunnel. It has been estimated that about 25 % of the injected naphthionate flew out through the Osapska Reka spring and about 5 % through the Boljunec/ Bagnoli springs. Based on this research, proper monitoring of any potential negative impacts of the new railway line will be made possible. The study presents an approach to better planning of hazard control of traffic routes in complex and highly karstified rock settings.
Downloads
References
Alija, S., Torrijo, F. J. & M. Quinta-Ferreira, 2013: Geological engineering problems associated with tunnel construction in karst rock masses: the case of Gavarres tunnel (Spain).- Engineering geology, 157, 103-111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.02.010
ARSO 2019: Slovenian Environment Agency, Interactive weather.- [Online] Available from: https://meteo.arso.gov.si/met/en/app/webmet/ [Accessed 16th February 2019].
ARSO 2020: Slovenian Environment Agency, Archive hydrological data.- [Online] Available from: http://vode.arso.gov.si/hidarhiv/pov_arhiv_tab.php [Accessed 6th January 2020].
Atlas okolja 2020: Environmental Atlas, Tracer tests data.- [Online] Available from: http://gis.arso.gov.si/atlasokolja/profile.aspx?id=Atlas_Okolja_AXL@Arso [Accessed 20th January 2020].
Benischke, R., Goldscheider, N. & C. Smart, 2007: Tracer techniques.- In: Goldscheider, N. & D. Drew (eds) Methods in karst hydrogeology. Taylor&Francis, pp. 161-184, London.
Boegan, E., 1938: Il Timavo. Studio sull’idrologia carsica subaerea e sotterranea.- Mem. Ist. It. Speleol., pp. 251, Trieste.
Barberá, J.A., Mudarra, M., Andreo, B. & Andreo, B., & B. De la Torre, 2018: Regional-scale analysis of karst underground flow deduced from tracing experiments: examples from carbonate aquifers in Malaga province, southern Spain.- Hydrogeol Journal, 26, 23–40. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-017-1638-5
Calligaris C., Galli M., Gemiti F., Piselli S., Tentor M., Zini L. & F. Cucchi, 2019: Electrical Conductivity as a tool to evaluate the various recharges of a Karst aquifer.- ROL, 47, 13-17.
Calligaris C., Mezga K., Slejko F.F., Urbanc J. & L. Zini, 2018: Groundwater characterization by means of conservative (d18O and d2H) and non-conservative (87Sr/86Sr) isotopic values: the Classical Karst Region aquifer case (Italy–Slovenia).- Geosciences, 8, 321. doi:10.3390/geosciences8090321
Cucchi, F., Zini, L. & C. Calligaris (eds), 2015: Le acque del Carso Classico / Vodonosnik klasičnega Krasa. Progetto/Projekt HYDROKARST.- Edizioni Università di Trieste, pp. 181, Trieste.
Gabrovšek, F., Knez, M., Kogovšek, J., Mihevc, A., Mulec, J., Otoničar, B., Perne, M., Petrič, M., Prelovšek, M., Slabe, T., Šebela, S., Turk, J. & N. Zupan Hajna, 2015: The Beka-Ocizla Cave System (Cave and Karst Systems of the World).- Springer, pp. 102, Cham [etc.]. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-04456-9_2
Galli M (2012) I traccianti nelle ricerche sul Timavo. Edizioni Università di Trieste, Trieste
Gemiti, F., 1984a: La portata del Timavo alle risorgive di S. Giovanni di Duino.- Annali Gruppo Grotte Ass. XXX Ott., 7, 23-41.
Gemiti, F., 1984b: Nuova e originale prova di marcatura delle acque del Timavo.- Annali del Gruppo Grotte dell’Associazione Trenta Ottobre, 7, 43-62.
Gemiti, F., 1995: Portata liquida e portata solida del Timavo alle risorgive di S. Giovanni di Duino.- Hydrores, 13, 75-88.
Gemiti F (1998) Marcatura delle acque del Timavo a seguito di un versamento di idrocarburi nella valle della Recca e interpretazione dell’evento mediante l’utilizzo di dati meteorologici, idrologici, idrochimici. Annali del Gruppo Grotte dell’Associazione Trenta Ottobre 10:93–104
Gemiti, F., 2004: Le sorgenti Sardos e l’approvvigionamento idrico della Provincia di Trieste.- Atti e Mem. Della Comm. E. Boegan, 39, 67-80.
Goldscheider, N., Hötzl, H. & K. Kottke, 2001: Microbiological decay of naphthionate in water samples as a source of misinterpretation of tracer tests.- In: Seiler, K.P. & S. Wöhnlich (eds.) Characterizing Groundwater Flow: Proceedings of the XXXI IAH Congress, Munich, Germany, 10-14 September 2001. CRC Press, 77-81, Munich.
Goldscheider, N., Meiman, J., Pronk, M. & C. Smart, 2008: Tracer tests in karst hydrogeology and speleology. International Journal of Speleology, 37, 27-40. https://doi.org/10.5038/1827-806X.37.1.3
Hötzl, H., 1999: Industrial and urban produced impacts.- In: Drew, D. & H. Hötzl (eds.) Karst hydrogeology and human activities, Impacts, consequences and Implications, International contributions to hydrogeology. A.A. Balkema, pp. 81-185, Rotterdam.
Jin, X., Li, Y., Luo, Y. et al., 2016: Prediction of city tunnel water inflow and its influence on overlain lakes in karst valley.- Environmental Earth Sciences, 75, 1162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5949-y
Jurkovšek, B., Biolchi, S., Furlani, S., Kolar-Jurkovšek, T., Zini, L., Jež, J., Tunis, G., Bavec, M. & F. Cucchi, 2016: Geology of the Classical Karst Region (SW Slovenia – NE Italy).- Journal of maps, 12/51, 352-362. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/17445647.2016.1215941
Käss, W., 1998: Tracing technique in geohydrology.- A.A, Balkema, pp. 581, Brookfield, Rotterdam.
Knez, M., Umek, U., Gabrovšek, F., Mihevc, A., Mulec, J., Otoničar, B., Petrič, M., Pipan, T., Prelovšek, M., Ravbar, N., Slabe, T., Šebela, S., Zupan Hajna, N., Blatnik, M., Kogovšek, B., Kukulajn, L., Mayaud, C., Aljančič, M., Drame, L., Drole, F. & M. Zadel, 2019: Krasoslovna interpretacija raziskav : zbirno poročilo : izvedba dopolnilnih strukturno geoloških, hidrogeoloških, krasoslovnih in geotehniških raziskav za PZI drugega tira železniške proge med Divačo in Koprom : drugi tir železniške proge Divača-Koper.- Gradbeni inštitut ZRMK, Ljubljana.
Kogovšek, J., 2011: Threats to the karst water sources from traffic in normal conditions.- In: Knez, M., Petrič, M. & T. Slabe (eds.) Karstology and development challenges on karst, Water. ZRC Publishing, pp. 47-64, Ljubljana.
Kogovšek, J. & M. Petrič, 2004: Advantages of longer-term tracing —three case studies from Slovenia.- Environmental Geology, 47, 76-83.
Kogovšek, J. & M. Petrič, 2011: Spillages of hazardous substances endanger karst waters.- In: Knez, M., Petrič, M. & T. Slabe (eds.) Karstology and development challenges on karst, Water. ZRC Publishing, pp. 76-83, Ljubljana.
Krivic, P., Bricelj, M., Trišič, N. & M. Zupan, 1987: Sledenje podzemnih vod v zaledju izvira Rižane.- Acta carsologica, 16, 83-104.
Krivic, P., Bricelj, M. & M. Zupan, 1989: Podzemne vodne zveze na področju Čičarije in osrednjega dela Istre.- Acta carsologica, 18, 265-295.
Li, X. & Y. Li, 2014: Research on risk assessment system for water inrush in the karst tunnel construction based on GIS: case study on the diversion tunnel groups of the Jinping II Hydropower Station.- Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 40, 182-191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2013.10.005
Mesarec, D., 2011: Davorjevo brezno.- Jamar, 7, 20-26.
Massei, N., Wang, H. Q., Field, M. S., Dupont, J. P., Bakalowicz, M. & J. Rodet, 2006: Interpreting tracer breakthrough tailing in a conduit-dominated karstic aquifer.- Hydrogeology Journal, 14/6 , 849-858. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-005-0010-3
Meus, P., Käss, W. & P.A. Schnegg, 2006: Background and detection of fluorescent tracers in karst groundwater.- Hidrogeologia y Aguas Subterraneas, 18, 65-75.
Meus, P., Schnegg, P. A., Frippiat, C. & J. Monfort, 2014: Promises and limitations in the use of sulfonates colourless tracers in hydrogeology.- Geologica Belgica, 17/1, 90-95.
Mosetti, F., 1965: Nuova interpretacione di un esperimento di marcatura radioattiva del Timavo.- Bolletino di Geofisica teorica et applicata, 7/27, 218-243.
Peric B., 2012: Karst water course tracing between ponor and springs: the Reka river example, Kras/Carso, SW Slovenia-NE Italy. In: Šebela S., Peric B., Fabbricatore A. & D. Cergna (eds.) International Congress on "Scientific Research in Show Caves", 13th to 15th September 2012 Postojna, pp. 32-33.
Petrič, M. & J. Kogovšek, 2011: Assessment of the possible impact of the construction of the Divača-Koper rail-way line on the quality of karst waters.- In: Prelovšek, M. & N. Zupan Hajna (eds.) Pressures and protection of the underground karst: cases from Slovenia and Croatia. Karst Research Institute ZRC SAZU, pp. 138-146, Postojna.
Placer, L., Vrabec, M. & B. Celarc, 2010: The bases for understanding of the NW Dinarides and Istria Peninsula tectonics.- Geologija, 53/1, 55-86. doi:10.5474/geologija.2010.005
Raithel, M., Baumbusch, J. & S. Kielbassa, 2016: Construction of the New High-Speed Railway Line Ulm–Wendlingen in Karstifed Rock.- Procedia engineering, 143, 1144-1151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2016.06.139
Timeus, G., 1928: Nei misteri del mondo sotterraneo.- Alpi Giulie, 29, 1-38.
Turpaud, P., Zini, L., Ravbar, N. et al., 2018: Development of a Protocol for the Karst Water Source Protection Zoning: Application to the Classical Karst Region (NE Italy and SW Slovenia).- Water Resources Management, 32, 1953-1968. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-017-1882-4
Urbanc J., Mezga K. & L. Zini, 2012: An assessment of capacity of Brestovica – Klariči Karst Water Supply (Slovenia)”.- Acta carsologica, 41/1, 89-100.
Vincenzi, V., Gargini, A., Goldscheider, N. et al., 2014: Differential Hydrogeological Effects of Draining Tunnels Through the Northern Apennines, Italy.- Rock Mech Rock Eng, 47, 947-965. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-013-0378-7
Zhou, W. & B.F. Beck, 2005: Roadway construction in karst areas: management of stormwater runoff and sinkhole risk assessment.- Environmental Geology, 47/8, 1138-1149.
Zini L., Visintin L., Cucchi F. & W. Boschin, 2011: Potential impact of a proposed railway tunnel on the karst environment: The example of Rosandra valley, Classical Karst Region, Italy-Slovenia.- Acta carsologica, 40/1, 207-218.
Zini L., Calligaris C. & E. Zavagno, 2013: Classical Karst hydrodynamics: a sheared aquifer within Italy and Slovenia.- In: Castellarin, A. et al. (eds.) Evolving Water Resources Systems: Understanding, Predicting and Managing Water‐Society Interactions. IAHS Publication, 364, pp. 499‐504.
Zini, L., Calligaris, C. & Cucchi, F., 2015: The challenge of tunnelling through Mediterranean karst aquifers: the case study of Trieste (Italy).- Environmental Earth Sciences, 74, 281-295. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4165-5
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Authors guarantee that the work is their own original creation and does not infringe any statutory or common-law copyright or any proprietary right of any third party. In case of claims by third parties, authors commit their self to defend the interests of the publisher, and shall cover any potential costs.
More in: Submission chapter




