Transport and consumption of organic detritus in a neotropical limestone cave
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3986/ac.v41i1.54Keywords:
cave, detritus processing, energy flowAbstract
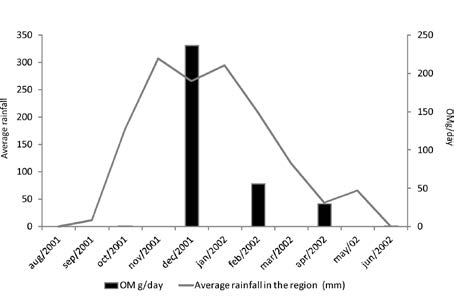
Caves are permanently aphotic environments, a fact that precludes the occurrence of photosynthetic organisms. In these systems the resource is allochthonous, coming mainly from the surrounding epigean environment, being imported by physical and biological agents. Even knowing about the importance of the organic allochthonous resources in caves, little is known of their importation and processing. The present work had as an objective, the measuring the coarse particulate organic matter processing and import rates in the subterranean environment. The cave studied was Lapa da Fazenda Extrema I, limestone cave, located in Brazilian savanna biome. Through bimonthly collections, it was observed that the organic detritus penetrated into the cave in low amounts in dry season and high amounts in rainy season. The processing of the organic plant matter in the aquatic hypogean environment was moderate (K-day=0.025), in the epigean environment the processing was predominantly slow (K-day =0.0104). The detritus commonly brought to the interior of the cave were large woods (58.18 g/day), followed by leaves and fragmented material (12.76 g/day), fruits and seeds (0.0069 g/day), animal carcasses (0.002 g/day) and roots (0.001 g/day). The highest richness and abundances of invertebrates were found in the same periods in which there were the highest rates of organic matter import to the cave.
Keywords: cave, detritus processing, energy flow.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Authors guarantee that the work is their own original creation and does not infringe any statutory or common-law copyright or any proprietary right of any third party. In case of claims by third parties, authors commit their self to defend the interests of the publisher, and shall cover any potential costs.
More in: Submission chapter




