Groundwater Recharge Assessment in the Karstic Aquifers of North Khorasan, Iran in APLIS Method
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3986/ac.v46i2-3.4740Keywords:
Groundwater resource management, Recharge, APLIS, GIS, karst, North KhorasanAbstract
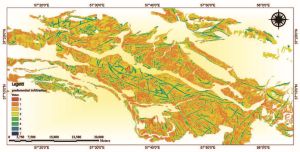
In order to optimize consumption, maintenance and control of underground water, an estimation of the groundwater recharge is highly important. Therefore, this research investigates the aquifers in North Khorasan province using APLIS (Applied Physics Laboratory Ice Station) based on a GIS. For this purpose, several significant hydrogeological parameters affecting groundwater recharge including altitude, slope, lithology, soil type and infiltration are considered. Therefore, corresponding layers for these parameters were provided and prioritized. In the end and after integrating the data, the recharge rate was measured qualitatively and different regions were mapped accordingly. The results indicate that the annual average values on a 30-year timescale in karst formations of the North Khorasan vary between 103 mm and 362 mm, with the mean value of 192 mm. Minimum, maximum and mean recharge rates of aquifer in the study area are 42 %, 73 % and 54 %, respectively. Also, aquifer recharge potential in 83 % of the karst formations is moderate while it is high for the remaining. Low recharge regions correlate to lower karst limestone and dolostone areas in the lower altitudes while high recharge regions represent upper karst limestone and dolostone areas, especially in the high altitudes.
Key words: Groundwater resource management, Recharge, APLIS, GIS, karst, North Khorasan.
Ocenjevanje napajanja podzemne vode v kraških vodonosnikih v severnem Horasanu, v Iranu, z uporabo metode APLIS
Za optimizacijo porabe, vzdrževanja in nadzora nivoja podzemne vode je ocena napajanja vodonosnika zelo pomembna. Zato raziskava z uporabo metode APLIS, ki temelji na GIS, raziskuje vodonosnike v provinci Severni Horasan v Iranu. Pri tem smo upoštevali več pomembnih hidrogeoloških parametrov, ki vplivajo na napajanje vodonosnika, vključno z nadmorsko višino, naklonom, litologijo, tipom tal in infiltracijo. Za vsakega od parametrov smo pripravili informacije v ustreznih oblikah. Po obdelavi in integraciji podatkov smo izračunali hitrost polnjenja vodonosnika. Različne regije smo ustrezno ovrednotili. Rezultati kažejo, da se v kraških formacijah Severnega Horasana letne povprečne vrednosti v 30-letnem časovnem obdobju gibljejo med 103 mm in 362 mm, s povprečno vrednostjo 192 mm. Najmanjše, najvišje in povprečne stopnje polnjenja vodonosnika v študijskem območju so 42-, 73- in 54-odstotne. Tudi potencial polnjenja vodonosnika je v 83-odstotnih kraških formacij ocenjen kot zmeren, za preostale predele je ocenjen kot visok. Območja z nizkim potencialom polnjenja so povezana z nižje ležečimi zakraselimi apnenci in dolomiti, višje ležeča območja predstavljajo apnenci in dolomiti z višjim potencialom polnjenja.
Ključne besede: upravljanje podzemnih vodnih virov, napajanje, APLIS, GIS, kras, Severni Horasan.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Authors guarantee that the work is their own original creation and does not infringe any statutory or common-law copyright or any proprietary right of any third party. In case of claims by third parties, authors commit their self to defend the interests of the publisher, and shall cover any potential costs.
More in: Submission chapter




