The effects of agricultural activities and atmospheric acid deposition on carbonate weathering in a small karstic agricultural catchment, Southwest China
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3986/ac.v45i2.4507Keywords:
carbonate weathering, karst groundwater, agricultural activities, atmospheric acid deposition, Qingmuguan, Southwest ChinaAbstract
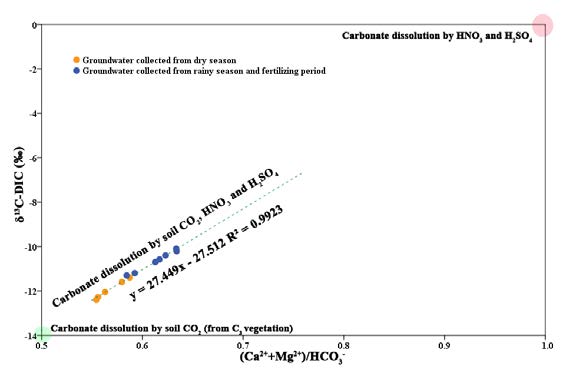
In order to quantify the sources and fluxes of DIC, the effects of the use of N-fertilizers and acid deposition on carbonate weathering have been quantified by hydrochemistry and δ13CDIC of groundwater in Qingmuguan underground river system (QURS) – a small karstic agricultural catchment of Southwest China. The results show that: (1) the significant temporal variations for major element concentrations and δ13CDIC of groundwater in different months were observed, especially, of which the groundwater showed significant high concentrations of DIC, Ca2+, Mg2+, NO3−, SO42− and δ13CDIC in rainy season and fertilizing period in the QURS; (2) the contributions of carbonate dissolution by carbonic acid to total concentrations of (Ca2++Mg2+) and HCO3− of groundwater in different months averaged 68.5 % and 81.0 %, respectively. While the contributions of carbonate dissolution by nitric acid originated from the use of N-fertilizers and atmospheric acid deposition to total concentrations of (Ca2++Mg2+) and HCO3− of groundwater in different months averaged 11.1 % and 6.7 %, respectively, and the contributions of carbonate dissolution by sulphuric acid originated from the atmospheric acid deposition to total concentrations of (Ca2++Mg2+) and HCO3− of groundwater in different months averaged 20.4 % and 12.3 %, respectively; (3) the δ13CDIC increased obviously with (Ca2++Mg2+)/HCO3− of groundwater in the rainy season and fertilizing period indicated that the use of N-fertilizers and atmospheric acid deposition should be responsible for the elevated the δ13CDIC and the molar ratio of (Ca2++Mg2+)/HCO3− of groundwater in the QURS.
Key words: carbonate weathering, karst groundwater, agricultural activities, atmospheric acid deposition, Qingmuguan, Southwest China.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Authors guarantee that the work is their own original creation and does not infringe any statutory or common-law copyright or any proprietary right of any third party. In case of claims by third parties, authors commit their self to defend the interests of the publisher, and shall cover any potential costs.
More in: Submission chapter




