Karst Types in Bulgaria
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3986/ac.v32i1.360Povzetek
Kras v Bolgariji obsega 26 170 km2 oziroma 22,7 % celotnega ozemlja. Kraški vodni viri so ocenjeni na 2,3 milijarde m3 , kar predstavlja 11,6 % vseh vodnih virov v državi. Zanimanje za bolgarski kras se je povečalo v zadnjih letih zaradi reševanja vsakdanjih vprašanj. Za ta kras je značilna velika raznolikost zaradi prepletanja različnih dejavnikov (geoloških, tektonskih, geomorfoloških, hidroloških in hidrogeoloških, klimatskih, itd.) in skladno z geodinamičnim razvojem tega dela Evrope. Pričujoče delo predstavlja novo delitev krasa v Bolgariji. Avtorica loči sledeče tipe: ravninski kras (Donavska nižina), morski kras, v ravninskega spremenjeni morski kras in ravninsko-morski kras (Črnomorska podvodna in kopna ravnina); planotasti kras (Predbalkan) in gorski kras. Posebej obravnava kraška močvirja in kraške pojave, ki so jih povzročili potresi v geološki preteklosti. Kot primer so predstavljeni tudi modeli različnih tipov krasa, njihov nastanek, dinamika, vpliv kamninske strukture, medsebojni odnosi, itd.
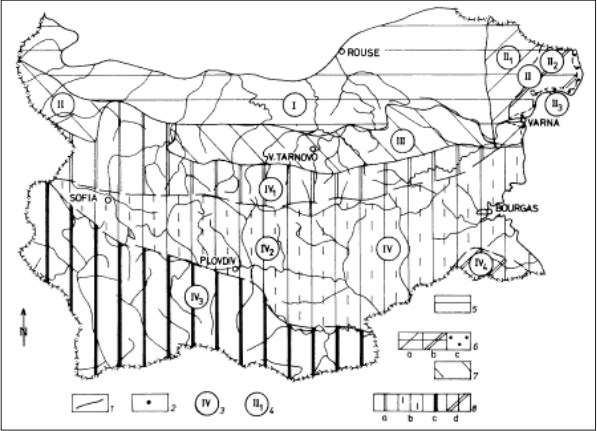
The karst in Bulgaria occupies an area of 26 170 km2 or 22.7 % of the territory of the country. The karst water resources are estimated to be 2.3 billion m3 or 11.6 % of the total water resources of the country. The interest in karst in Bulgaria has become higher during the last years because there are a number of practical problems that have to be solved. Karst in Bulgaria is characterized by great diversity due to the complex combination of factors (geological, tectonic, geomorphologic, hydrological and hydrogeological, climatic, etc.) and to the geodynamic development of this part of Europe. This work presents a new zoning of karst in Bulgaria. The following types have been distinguished: plain karst (the Danubian Plain); marine and transformed marine karst into plain and plain-marine karst (Black Sea subaqual and subareal plain); plateau-like karst (the Fore Balkan) and mountainous karst. The karst wetlands and karst phenomena provoked by paleoearthquakes are separately outlined and sample models for the different karst types, genesis, dynamics, lithostructural control, relations, etc. are presented.
Prenosi
Prenosi
Objavljeno
Kako citirati
Številka
Rubrike
Licenca
Avtorji jamčijo, da je delo njihova avtorska stvaritev, da v njem niso kršene avtorske pravice tretjih oseb ali kake druge pravice. V primeru zahtevkov tretjih oseb se avtorji zavezujejo, da bodo varovali interese založnika ter da bodo povrnili morebitno škodo.
Podrobneje v rubriki: Prispevki




