Human Impact on Karst Terrains, with Special Regard to Sylviculture in Hungary
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.3986/ac.v32i2.346Abstract
V sestavku so predstavljene spremembe, nastale na madžarskem krasu kot posledica človekove dejavnosti, posebno izkoriščanja gozda. Delovanje geo-ekosistema na krasu je v veliki meri odvisno od odnosov podnebje – prst – rastje, kar vpliva na hitrost razvoja krasa. Večina krasa na Madžarskem je vključenega v gospodarjenje z gozdovi. Sajenje neustreznih gozdnih sestojev ima lahko kot posledico spreminjanje klime in prsti, kar vodi k spremembam intenzivnosti korozije. Prispevek obravnava spremembe gospodarjenja z gozdom v narodnem parku Aggtelek, ki je na seznamu svetovne naravne dediščine, in predlaga ustreznejšo rabo tal.
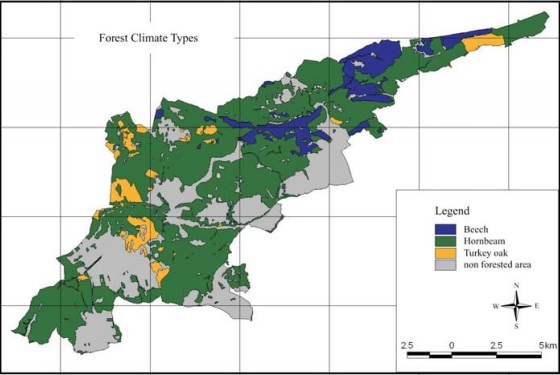
This study represents the changes of Hungarian karst terrains due to human impacts paying special attention to sylviculture. The functioning of the karst geo-ecosystem is considerably determined by the climate-soilvegetation system, which will influence the dynamism of karst development. Most of the Hungarian karst terrains are the scene of sylviculture. The planting of non-adequate forest associations resulted the alteration of climate and soils, which resulted in a change of the intensity of karst corrosion. This paper focuses on the change of sylviculture in the Aggtelek National Park, a World Heritage site, and makes suggestions for optimal land use.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Authors guarantee that the work is their own original creation and does not infringe any statutory or common-law copyright or any proprietary right of any third party. In case of claims by third parties, authors commit their self to defend the interests of the publisher, and shall cover any potential costs.
More in: Submission chapter




